What’s the best way to communicate with your boss? Open, honest, face-to-face conversation, of course.That would seem to fly in the face of Tell Your Boss Anything, a Web site designed expressly for sending anonymous messages. But it’s not really about giving ol’ Scrooge a piece of your mind; rather, the site appears to have constructive motives.
To get started, you enter your own “trusted” email address (more on that in a bit), then your boss’ address. Next, you create a subject line by filling in the blanks: “I feel ____ about ____.”
Within that first blank, you can choose words like happy, frustrated, irritated, confused, and proud. The words that go in the second blank are up to you.
Then you compose your email. When you click Tell my boss, your message gets delivered anonymously. But here’s the thing: Your boss can reply, and that reply will come to your aforementioned email address — all the while keeping your identity private.
The site cautions you to be “polite, respectful, and helpful,” and indeed nothing about Tell Your Boss Anything suggests that it’s aimed at telling a person off. The idea is more to express yourself in a way that you might not feel comfortable doing otherwise.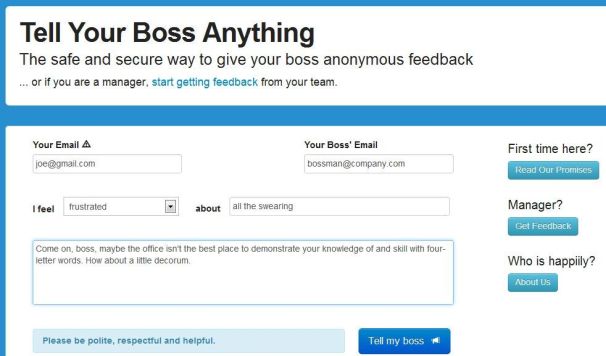
That could prove valuable if your boss is the type who doesn’t typically welcome open, honest, face-to-face communication. On the flipside, I think most bosses would likely be ticked off by an anonymous email from an employee, even one that was positive. What’s more, there’s always the risk that the boss will somehow “know it was you,” which might land you in hot water.
The real value here is for bosses themselves, who can use Tell Your Boss Anything to invite anonymous feedback from employees. It’s like a digital version of the suggestion box, a way to let the team know they can communicate with you without fear of reprisal.
Personally, I have no use for Tell Your Boss Anything, because my bosses are all awesome, and I have no qualms about telling them to their faces. Or, you know, by way of a blog post.
But what do you think? Would you ever use a service like this, either as a boss or an employee?
How to Send Your Boss an Anonymous Email
How Microsoft Surface Stacks Up Against Its Tablet Competition
How do the specs for the upcoming Microsoft Surface for Windows RT and Surface for Windows Pro compare with the Apple iPad? Here’s what we know.  Surface will change your expectations of what you can do with your tablet. First and foremost, you are no longer buying into a dedicated mobile OS and its corresponding app ecosystem. Instead, you’ll be able to buy one app and use it on both a tablet and a Windows 8 laptop or desktop PC.
Surface will change your expectations of what you can do with your tablet. First and foremost, you are no longer buying into a dedicated mobile OS and its corresponding app ecosystem. Instead, you’ll be able to buy one app and use it on both a tablet and a Windows 8 laptop or desktop PC.
While the Metro face of the two Surfaces will be the same, the hardware flavors are fundamentally different. Surface RT will compete most directly with Apple’s iPad and the current crop of Android tablets, all of which run on power-efficient ARM-based processors. And Surface Pro—though still a tablet—targets Ultrabooks and other ultraportable laptops.
Click on the chart below for a comparison of the two Surface models with other tablets.
Surface RT vs. the iPad and Android Tablets
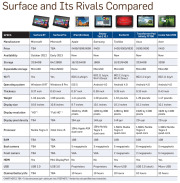 Tech specs: Surface RT comes with a USB 2.0 port standard (critical for connecting external storage and peripherals), along with a MicroSD card slot and Micro-HDMI video out. Most Android tablets have a MicroSD card slot and a Micro-HDMI port as well, but very few have a full-size USB port. Apple’s iPad famously has no ports, with the sole exception of its proprietary dock connector.
Tech specs: Surface RT comes with a USB 2.0 port standard (critical for connecting external storage and peripherals), along with a MicroSD card slot and Micro-HDMI video out. Most Android tablets have a MicroSD card slot and a Micro-HDMI port as well, but very few have a full-size USB port. Apple’s iPad famously has no ports, with the sole exception of its proprietary dock connector.
At the chip level, Nvidia’s Tegra 3 ARM processor powers the Surface RT. Most Android tablets run a version of the Tegra 3, as well, or they use another ARM-based processor. The iPad carries Apple’s own processor, which is also based on the ARM architecture.
Click for a full-size view of the chart.Storage on the Surface RT is similarly upscale, with a minimum of 32GB. The iPad and most Android tablets start at just 16GB. Among Android tablets, Asus’s Transformer Pad Infinity TF700 and Acer’s Iconia Tab A700 are the two exceptions, with 32GB baseline models.
Screen and resolution: Microsoft lists the RT’s display as “HD” rather than as “Full HD,” which likely translates into a resolution of just 1366 by 768 pixels. That won’t compete with the iPad’s Retina display, or even with those of Android tablets such as the Transformer Pad Infinity TF700 and the Iconia Tab A700 (both with resolutions of 1920 by 1200 pixels). The Surface RT’s optically bonded display, which eliminates the annoying air gap between the screen and the glass, should help overcome its resolution shortfall. Microsoft does cite its ClearType font-display technology, but we won’t know how much ClearType can compensate for the gap in pixel density until we have the Surface tablet in hand.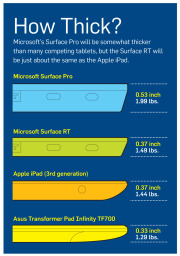 Click for a full-size view of this chart.Physical specs: Microsoft didn’t supply complete numbers, but it did say Surface RT should be about 0.37 inch thick—thinner than many competing tablets and in a dead heat with Apple’s iPad. Current estimates put the Surface RT’s weight at 1.49 pounds, or 0.05 pound heavier than the current iPad. That’s a negligible difference, but the iPad itself got heavier this year, while Android tablets are consistently moving in the other direction, as consumers have come to expect. At 1.49 pounds, the Surface will be about 0.2 pound heavier than the Toshiba Excite 10 or the Asus Transformer Pad Infinity.
Click for a full-size view of this chart.Physical specs: Microsoft didn’t supply complete numbers, but it did say Surface RT should be about 0.37 inch thick—thinner than many competing tablets and in a dead heat with Apple’s iPad. Current estimates put the Surface RT’s weight at 1.49 pounds, or 0.05 pound heavier than the current iPad. That’s a negligible difference, but the iPad itself got heavier this year, while Android tablets are consistently moving in the other direction, as consumers have come to expect. At 1.49 pounds, the Surface will be about 0.2 pound heavier than the Toshiba Excite 10 or the Asus Transformer Pad Infinity.
The Surface tablet’s design is unique. It features a comfortably angled bezel created with ergonomics in mind; a balanced arrangement of internal components that make Surface feel lighter; and a built-in kickstand for conveniently using Surface in a variety of scenarios.
Productivity: In this respect Surface RT is likely to shine. Unlike Apple’s iOS and Google’s Android, Microsoft’s Windows 8 provides the ability to view two apps at a time on one screen, as well as having additional apps multitasking in the background. This flexibility is closer to what users are accustomed to having on a desktop or laptop computer. Plus, Surface RT will include Office Home and Student 2013 RT (with Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and OneNote).
Surface Pro vs. Ultrabook Laptops and Windows 7 Tablets
Tech specs: Surface Pro will come with 64GB or 128GB of storage and an Intel Core i5 CPU (Microsoft has not yet revealed the clock speed). By contrast, Ultrabooks have anywhere from 128GB to 320GB of solid-state or hard-drive storage, and feature Intel Core i3, Core i5, or Core i7 CPUs. Microsoft hasn’t disclosed how much memory its Surface Pro will have; Ultrabooks average 4GB of RAM, comparable to what you’d find on an ultraportable or all-purpose laptop. Surface Pro outdoes most Ultrabooks, though, with a MicroSDXC card slot, a USB 3.0 port, a Mini DisplayPort for video output, and a dual digitizer for digital inking with a stylus.
An example of a Surface screen; click for a full-size view.Screen and resolution: Preliminary specs simply state that Surface Pro has a “Full HD” 10.6-inch display, which would suggest a display resolution of at least 1920 by 1200 pixels. That minimum spec would put it on a par with the best Android tablets from Asus and Acer, but those displays are half an inch smaller, so they have a higher pixel density. And none of the Android models compares with the 9.7-inch Apple iPad at 2048 by 1536 pixels. Like Surface RT, Surface Pro will also feature Microsoft’s ClearType (standard in Windows 8). Physical specs: Surface Pro’s overall physical design is the same as Surface RT’s; but this model will be thicker, at 0.53 inch. Nonetheless, Surface Pro looks more stylish and snappy than current Windows 7 slates, and it’s thinner than many Ultrabooks. Surface Pro’s weight is estimated at 1.99 pounds, which is significantly lighter than the average 3- to 4-pound Ultrabook and comparable to current Windows 7 tablets.
Physical specs: Surface Pro’s overall physical design is the same as Surface RT’s; but this model will be thicker, at 0.53 inch. Nonetheless, Surface Pro looks more stylish and snappy than current Windows 7 slates, and it’s thinner than many Ultrabooks. Surface Pro’s weight is estimated at 1.99 pounds, which is significantly lighter than the average 3- to 4-pound Ultrabook and comparable to current Windows 7 tablets.
Productivity: Intel’s Core i5 is powerful enough to let you tinker in Photoshop, handle complex spreadsheets, or play games. Surface Pro won’t come with Microsoft’s Office apps, though. Still, with digital inking plus one of Microsoft’s keyboard cover options, Surface Pro could be the ultimate ultraportable. If you can make do with a 10.6-inch display, then you can benefit from Surface’s inherent flexibility.
How to Choose a New PC Case
We’ll show you how to find, buy, and build in a brand-new PC chassis.

If you aren’t a dedicated PC builder, the last thing you probably think about is your PC case. But there are a number of good reasons for moving to a new chassis: You might need space for more components; you might want more cooling; you might long for some fancy features such as clear side panels or glowing fans and lights; or you might be interested in upgrading your front-panel connectors to support the latest and greatest connection types.
Whatever your reason for considering a new shell, we’ll walk you through the process of selecting one–and we’ll look at how to move the parts and pieces from your old case into your new case smoothly and efficiently.
Choose a Suitable Case
PC cases fall into three broad categories: Budget, Midrange, and High-End. But a relatively inexpensive case isn’t necessarily worse than an expensive one.
Budget Bonanza

A typical budget case is inexpensive ($20 to $40), rectangular, and featureless. In other words, it’s a nondescript replacement case with few special features to help you fit more components into your rig, tidy up your cables, or installation your system’s current components easily.
Budget cases tend to be plain, functional, and utterly ordinary.
If you want the barest possible enclosure for your PC’s parts, have no interest in expanding your case’s features or available connections beyond what you currently have, or want to spend as little as possible on a new case, you go budget. You’ll get what you pay for with these models in this price range.
Midrange Medley
In this category, prices run from $75 to $200, and you’ll find considerable variation in design and construction.
Midrange cases typically offer handy features such as soundproofing, cable channels for routing wires, and extra connection ports.

These cases may have (or lack) a number of features that suit your needs. The most important variable to consider is case dimensions, since you’ll want to know at the outset that your new chassis can hold all of your system’s components without difficulty. Problems may arise if, for example, you have an extralong video card that won’t fit into a case because of its internal layout. If you have multiple cables, liquid cooling tubes, or huge CPU coolers to accommodate, triple-check that your PC parts will fit comfortably within a prospective new case before buying it.
Also, make sure that your new case can support all of your 3.5-inch and 5.25-inch devices. And don’t buy a three-bay case if your system uses a four-drive RAID array.
In appraising the raw design of the case, consider whether its accouterments–such as a big door covering the front panel, lighting effects that you can’t turn on and off manually, or a manual cooling bar that falls out of the case whenever you pop off the side panel–contribute more nuisance than neatness.
Will the case’s overall design be practical six months after you purchase it? If you buy a soundproof case in the winter, will your system be able to handle the hotter interior temperatures that occur during summertime? Keep the big picture in mind, and don’t let eye-catching details lead you astray.
Here are some other important questions to ask: What kind of connections come built into the case’s front panel (or sides, depending on its design)? Does the case deliver true internal headers for its connections or just pass-through cables? Are the case’s USB ports upside-down? Is the case screwless? Does it come with fans preinstalled? How loud are they when you fire up a system? What other fan configurations could you mount?
For liquid cooling enthusiasts, what size radiators does the case support? How easily could you mount one externally or internally? Does the case come with motherboard standoffs, or are they built into the motherboard tray? Can you remove the motherboard tray separately from the case? Can you install or tweak the backplane of a CPU cooler without having to remove the entire motherboard? What options does the case provide for managing the system’s cables?
High-End Heaven
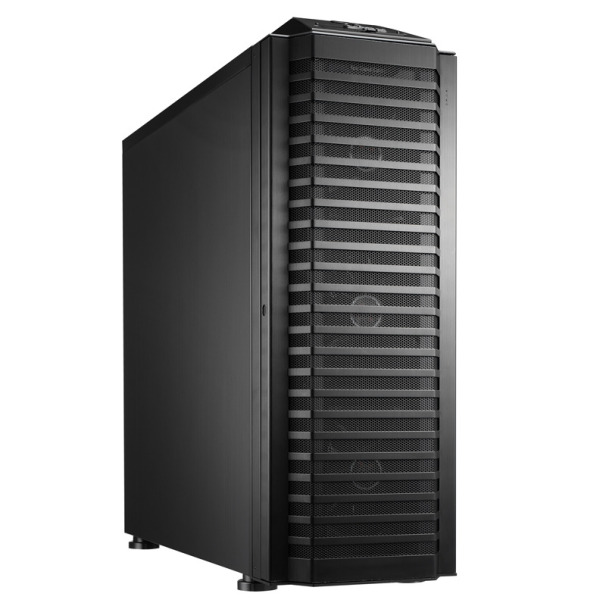

Once you break the $200 barrier, you have to deal with manufacturers who sometimes let their imaginations run wild, resulting in PC cases that may be flashier than they are functional. So don’t let an expensive case’s ingenious design blind you to potential shortcomings in its usefulness. A manufacturer may go to great lengths to craft a killer yet functional design for its unique chassis, or it may slap an outlandish design or a few gimmick features on a case that is unpleasant to work with.
The Lian-Li PC-P80NB is an ATX full-tower case roomy enough to hold every component you could dream of.
Cases at the high end of the spectrum may come with a ton of cooling, fan controllers, and other switchable features built directly into the chassis. Some may cover every inch of the inside surface with soundproof acoustic foam; others may come with water-cooling loops built into the chassis, like the Logisys CS8009BK. And finally, some cases may be expensive simply because they’re huge: The Lian-Li PC-P80NB, for example, can support 11 PCI devices and 10 hard drives, and comes with six preinstalled fans (five 14-centimeter fans, and one 12-centimeter fan). If that meets your PC building needs, buy it; otherwise, steer clear.
Next: Transfer your PC’s components to the new case.
Move Your PC Components From the Old Case to the New One
The process of transferring components from one case to another is in some ways simpler than the process of selecting the new case. Start with the components that you can easily uninstall, move, and install without affecting any others.
In a typical system build, I like to start by disconnecting all of the wires and power cables in my existing chassis so that I can get the rat’s nest out of the case before I try to remove individual components. Pull out the SATA cables and the power supply, and disconnect other wires inside the system. Then pop off your system’s side panels, remove your case’s front panel (if applicable), and remove your 5.25-inch optical drives. Depending on the design of your new case, you might be able to load these components into the new shell immediately–one reason I love tool-free case designs. Hard drives come next, and they merit the same treatment.
Many tool-free cases let you slot your components into place without using screws or removable case fixtures.
Next, remove your PCI devices, which might consist of a single discrete video card in some instances. Assuming that you aren’t running some fancy water-cooling setup, your old case should be empty of practically everything but the motherboard by now. Unscrew it and gently remove it from the case, gripping it by the edges.
If your new case doesn’t come with motherboard standoffs, screw them in–and install your motherboard’s I/O shield–before attempting to install the motherboard itself.
Once the motherboard is in place, I usually attach the system’s PCI devices, especially the video card; however, this approach may make for trickier access to SATA ports or other connectors, depending on the motherboard’s layout. On the other hand, waiting to install the video card can pose a bit of a challenge if the power cables on the power supply barely reach the top connectors on the motherboard.
Try to route as many cables as possible behind the motherboard, to keep them from cluttering up your case interior and restricting airflow.
Once all of your components are in place and you’re ready to start connecting cables, try to use your case’s built-in cable management options to maximum advantage. In most systems, the goal is to route as many cables as possible behind the motherboard (mashed up against the right side panel). For this purpose, cases that provide multiple routing holes around the motherboard tray or fasteners (for twist ties/Velcro strips/twine or the like) behind it can be immensely helpful. Minimizing clumps of cables in the middle of your PC will give the system better airflow.
Next, examine your case layout and verify whether you need to install the power supply at this stage. I recommend waiting until the last possible moment to install your power supply, to avoid having to deal with a bunch of loose power cables. Unfortunately, some cases make it hard to install your power supply after the motherboard is in place, so plan accordingly. Once you’ve installed the power supply and finished connecting all of the system’s cables, you should be finished.
Transferring components from one case to another isn’t especially difficult, even for computer newbies. For most people, the most time-consuming part of the operation involves cable management–unless you’re migrating a relatively tricky system build (such as one featuring a liquid cooling loop) to a case that may require some creative thinking to achieve the desired results.
Don’t be afraid of cases. Buy one. Build a system in one. You’ll be amazed at the options that await your consideration–including plenty of builder-friendly features–on today’s market of well-priced, well-designed chassis.
RIM Unveils Its New 4G BlackBerry PlayBook Tablet
Is this new PlayBook RIM’s last hurrah in the tablet competition? A new 4G BlackBerry PlayBook will go on sale next week, a year after Research In Motion introduced its first tablet. The updated 7-inch PlayBook will include 4G connectivity and 32GB of storage, but RIM has yet to name a price or a U.S. availability date.
The first in line to get their hands on the new PlayBook will be Canadians from August 9, via carriers Bell, Rogers, and Telus. “In the coming months” RIM also expects cellular-data enabled versions of the PlayBook to reach the U.S., Europe, and other countries. But even with the Canadian availability date coming up so quickly, RIM still hasn’t said how much the new PlayBook would cost.
If there’s no 4G LTE connectivity available in your area or carrier, RIM says the 4G LTE BlackBerry PlayBook tablet can automatically adjust to connect on a HSPA+ network.
Otherwise, there’s very little changed hardware-wise between the original PlayBook and the 4G model. The tablet still has a 7-inch 1024-pixel by 600-pixel resolution display, dual HD video cameras, HDMI capability, and stereo speakers. The processor is bumped up to 1.5GHz from 1GHz in the Wi-Fi-only model, there’s still 1GB of RAM on board, and you only get one storage option: 32GB.
One Last Chance?
RIM’s 4G BlackBerry PlayBook TabletThe 4G LTE BlackBerry PlayBook tablet could be the make or break device for RIM. Due to key software omissions at launch, such as the lack of a native email client, the PlayBook suffered from lackluster sales. In fact, RIM had to take a $485 million hit last year because it was sitting on a huge inventory of unsold tablets.
The arrival of much cheaper 7-inch tablets from the likes of Amazon did not help either, as they undercut the PlayBook by up to $300 (Amazon’s Kindle Fire is $199 while the PlayBook launched at $500, and then began to be heavily discounted).
There’s still hope for Research In Motion though. After several delays, the anticipated BlackBerry PlayBook OS 2.0 will ship with the new tablet. All the features you would expect are now there, including email, calendar, contacts, and video chat. But given the lack of any substantial improvements to the tablet (for example the $200 Google Nexus 7 has a higher-resolution display), adding 4G connectivity to the PlayBook might still be too little, too late for RIM.
Put an Old Phone to Good Use–Make it a Lego NXT Telepresence Robot
Aww, how cute. [Credit: Wolfgang Beer]Do you have an old Android phone stored away that you keep only for emergencies–or just aren’t sure what to do with it? You could breathe new life into the semi-retired handset by strapping it up to a Lego Mindstorms NXT set and turn it into a household security robot.
Wolfgang Beer developed the telepresence robot as a way of monitoring his home while he was
away. The robot cruises around the house and gathers images, and uses an HTC Magic phone connected to the NXT robot kit. The Android phone works as a controller for the robot, which can receive signals over the Internet and transmit the commands via Bluetooth to the NXT microcontroller.
The actual robot part of the build is pretty straightforward–it’s made up of a few bricks that holds the phone and and battery in place.
The robot picks up the commands through a small nanohttpd server, which also serves a HTML5 controls page. The controller page displays the on-board camera, and simple up, down, left, and right buttons for driving the robot.
http://www.youtube.com/embed/-z-3-gJjvxE?feature=player_embedded
Of course, while this is a good project to try out for yourself if you have an Android phone handy, it does require a fair bit of coding. Fortunately, Wolfgang has most of the code you will need available on his blog, or useful links to help.
Still, this is one pretty cool way of seeing what the cat is up to while you’re gone, or, if the worst does happen, at least startle a burglar into leaving your property.
Facebook Unveils New User-Generated Feature: Facebook Stories
The nearly 1 billion users (fewer, of course, if you don’t count all those bogus accounts) who use Facebook every day sure share a lot of stuff. However, a lot of it gets lost in the shuffle.
Mayank Sharma used Facebook to rebuild memories lost due to contracting meningitis.Not anymore thanks to a new feature called Facebook Stories.
The new site launched Thursday, and aims to showcase how Facebookers use the site in compelling ways. Each month features a different theme–the theme for August is “Remembering.”
This month’s feature tells the story of 27-year-old Mayank Sharma, from New Delhi, India, who lost his memory after contracting a rare form of meningitis. Sharma used Facebook to rebuild the memories he had lost due to contracting the disease. He credits Facebook with helping him “rebuild” his life.
While Sharma’s story is an extreme case, it shows the type of stories Facebook is looking for.
What Facebook Looks For
Other showcased features include a group of residents in Guelph, Ontario using civic pride and the town’s collective memory to save an important local building, a selection of books to read, musical playlists courtesy of Spotify, and selected articles from the New Yorker Magazine.
Facebook says the books, playlists and New Yorker features will be updated on a monthly basis.
Highlights on Facebook Stories
Another monthly feature is the Infographic, which is updated each month to match the theme. This month’s edition looks at what we share most. According to Facebook, the most common story shared on the timeline is on travel, which makes up 42% of such stories.
That was followed by stories on moves, posted 18 percent of the time, and the ever-popular relationship change, which appeared 10 percent of the time.
These first stories were handpicked by Facebook, but future editions will include submissions from users. Those who think they might have an interesting story to share with the world via Facebook Stories can submit theirs through an online form.
Avoid Facebook Disasters
Ignoring Facebook’s privacy options can trip up users in a number of ways. Avoiding Facebook and Twitter Disasters
Take some practical steps to control what others see about you on Facebook and Twitter.Ignoring Facebook’s privacy options–some of them fairly new and not well known–can trip up the social-networking site’s users in a number of ways. Here are some that everyone who has a Facebook account should be aware of.
Oversharing With the Boss
The disaster:Ann played hooky from work, calling in sick, and spent the day sunbathing, updating her Facebook status on her laptop all the while. The next day, her boss confronted her with the evidence that she wasn’t really ill, causing severe embarrassment and a reprimand (plus a day of docked pay).
The solution: In this day and age, professional and personal lives often become intertwined, and Facebook can be ground zero for this. You might momentarily forget that you have “friended” your boss, and that he has the same access to your ramblings on Facebook as do your real-life drinking buddies. But you can change that.
Using Facebook’s Lists settings might have made the most sense for Ann. Lists, one of the newer features of Facebook, allow you to organize people into groups and then assign each group different levels of access to your information on Facebook.
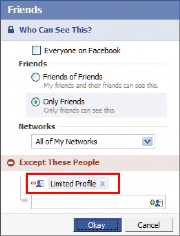
‘Limited Profile’ is a default group for less-wanted contacts, but you’ll see need to specify what rights those who are in it should have.Lists let you set who can see what on your profile. For example, if you’ve added someone as a friend but aren’t sure about them, you can relegate them to a list that you name “Limited Profile,” which will limit how much of your profile that person may view and interact with. You can also create lists for work, school, special projects, or anything else, but by default the lists don’t change how your profile displays.
To work with Lists, click the Friends button (top bar) and +Create in the left column under Lists-or just put people on any list by using the ‘Add to list’ drop-down menu next to their name.
Next, you need to specify how much of your information on Facebook members of each list can see. To do this, visit the Privacy Settings page (hover over ‘Settings’ in the top right of the screen, and click Privacy Settings inside the box that pops up; or go to www.facebook.com/privacy), then select Profile. Here, select Customize…from the drop-down menu next to whichever section you’d like, and type the name of the list in the box under ‘Except These People’. For Ann, dropping her workmates into a “work” list and dialing down that group’s access to the bare minimum would have saved her a lot of trouble. Specifically, she should change the ‘Status and Links’ setting so as to exclude the Limited Profile list. (Note, however, that updates to your profile from third-party applications are generally not blocked by these privacy settings.)
UPDATE (4PM 6/24): With Facebook’s just-announced status publisher upgrade (now in beta), you will (or will soon) see an option (a gray lock with a dropdown menu) letting you control who sees these updates on an individual basis. For broad posts, “Everyone” will let the whole world (including Google and other off-Facebook locations) see the update. For more sensitive posts you can change the setting to “Friends” – or use fine-grained control through “Custom,” restricting the post to be visible only to certain friend lists.
He Knows Where You Live
The disaster:Getting far away from ex-boyfriend Bob wasn’t the main reason Mary moved to Pittsburgh, but it was one of the main benefits. So when Bob showed up at her new job, she was naturally disturbed. How did he find out where she was, she asked. “It was on your Facebook profile,” he replied.
The solution: All users have extremely fine-grained control over what gets on their Facebook page, but few take full advantage of these features.
The entry to all Facebook privacy settings is on this page. But thoroughly exploring all four of its subpages can take hours. (In this article, we’ll point you to some of the most important settings.)The controls are found in the Privacy Settings page under ‘Profile’, reachable as outlined above. Here you’ll find a list of ten items on your profile that you can turn on or off, each to a different group of Facebook users.
‘Profile’ lets you choose whether to block people from seeing anything beyond the most basic information (name and network) on your profile page, while ‘Basic Info’ allows viewing of gender, birthday, relationship status, and the like. ‘Personal Info’ opens the door a little wider-to your “about me” section, interests and favorites, and so on; ‘Status and Links’ controls who can see your latest status update. Most of the categories are self-explanatory (just click the question-mark icon if you need help) and can get pretty detailed. But this is also an advantage: If, like Mary, you don’t want to advertise where you work, you can turn off that detail here.
Also, click Save Changes at the bottom of any Facebook settings screen, or your settings will not be updated.
What should you change these settings to, then? Facebook offers numerous choices for each category: Everyone, My Networks and Friends, Friends of Friends, Only Friends, and Customize. Everyone is self-explanatory; My Networks and Friends is less inclusive, limiting profile viewing to anyone you’re friends with or with whom you share a network; Friends of Friends essentially gives you two degrees of openness instead of one; and Only Friends is exactly how it sounds.
The Profile settings under Privacy allow you to control which Facebook users can see your profile and which ones cannot.The Customize option gives you complete command over your network settings: You can limit viewing of your profile to certain networks and, in some cases, subsets of that network. Current students, for example, can prohibit faculty or other undergrads from viewing their profile. How much to lock things down is up to you. In Mary’s case, making her Profile visible to ‘Only Friends’ would have prevented an unpleasant surprise visit.
The Stalker Problem
The disaster:Jessica is worried about the creepy messages and Wall posts being left by some guy she doesn’t know but whose friend request she accepted. She doesn’t want to delete her account, but she does wish to get rid of the stranger and set her profile to be discovered only by those people she allows.
Illustration by Mick Wiggins The solution:First, Jessica should add the possible stalker to a Limited Profile list, as outlined earlier. If you have a hostile stalker, you can remove and/or block them: Go to the person’s profile page and then click the Remove from Friends option at the bottom of the left column.
If the person persists in friend requests, you can block the stalker altogether by going to the Privacy page and typing their name in the search box in the ‘Block People’ region. Standard Facebook-style search results will pop up; just click Block Person next to their name, and they won’t find you in a search, or view any part of your profile.
For a stronger level of privacy and security, you can temporarily “go dark” by making your profile virtually invisible. Go to the Privacy settings page and click Search. Set the Search Visibility drop-down selection to Only Friends. This tells Facebook not to show your profile in public searches on the site.
The Search Result Content section lets you choose whether to show photos or lists of friends and links. If you don’t want to be contacted at all, remove the check marks by both options.
You can also use the Public Search Listing option to allow or prevent your profile from appearing in major search engine results such as those of Google.
Avoid Twitter Disasters
As a social networking tool, Twitter is even more open than Facebook–which is all the more reason to employ what safeguards you can on its network. Avoiding Facebook and Twitter Disasters
Take some practical steps to control what others see about you on Facebook and Twitter. The use, and uses, of Twitter seems to grow daily. Its role as a source of news on Iranduring that country’s current unrest has been widely reported, for example. For most people, however, Twitter is simply a convenient social networking tool, but as such, it is even more open than Facebook–which is all the more reason to employ what safeguards you can on its network. (Note: This article doesn’t cover such issues as the growing problem of spam on Twitter or reports of its use in phishing-like attacks.)
At the end of this article, we’ll also offer a brief guide to Twitter commands.
Twitter Never Forgets
The disaster:Nelson knows everyone who follows his Twitter feed and didn’t think much about trashing a coworker on the service. Months later, long after he’d forgotten about it, the coworker began to follow his tweets–and, with a little digging, found Nelson’s insult, creating an awkward office environment.
On Twitter, check the ‘Protect my updates’ box (highlighted above) to prevent your future tweets from being seen by anyone not approved as a follower. (Old tweets will still be accessible.) The solution:Unlike Facebook, Twitter has no mechanism for approving who follows you on the service, and anyone can read your full tweeting history. That is, unless you protect your updates: Click Settings and check the Protect my updatesbox. Your tweets now won’t be visible to anyone not approved as a follower. However, anything you’ve already sent out will stick around, especially on third-party Twitter interfaces.
Locking Out the Twitter Twits
The disaster:Vicky regularly tweets (nastily) about a former friend, and naturally doesn’t want that person to follow her on Twitter. How does she keep that person out before it becomes an issue?
Illustration by Mick Wiggins The solution:First, your account must be marked as ‘Protected’, as described in the preceding item. Then, assuming you know the person’s user name, simply block that user on Twitter. This option is on the profile page, in the ‘Actions’ section. It removes you from their Following list and prevents your updates from showing up on their page and from adding you to their Following list again. But your current friends can still copy and paste your tweets, or save them through screen captures.
The real lesson: It’s probably best not to bash anybody on Twitter if you’re afraid they’ll find out about it.
Linking Twitter With Facebook Can Be Trouble
The disaster:Dan thought he was being a good Web citizen and killing two birds with one stone by linking his Twitter account to his Facebook profile (visit apps.facebook.com/twitterto set it up for yourself–but finish reading this item first). The idea is sound enough: Update your Twitter status, and your Facebook status updates along with it, automatically. However, a Facebook connection isn’t always a good idea. If you’re live–tweeting, say, a sports event or a conference, you might post 20 tweets or more in an hour. That may fly on the rapid-fire Twitter, but on Facebook it’s over the line since it clogs up your friends’ news feeds.
The solution: In Dan’s case, a Twitter/Facebook link may not be appropriate, and he may be better off simply unlinking the two networks.
The best way to unlink is to browse to Facebook, click the Applications button on the bottom-left corner, and then select Applications. Find Twitter on this page and click the X to delete the app from your Facebook profile. (If you use a third-party application like TweetDeck to access Twitter, you’ll have to unlink your profile through that app.)
Be Careful What You Link To
The disaster:In one of his daily tweets, David linked to an article expressing a strong view on a controversial issue. Before he knew it, David was being bombarded with tweets rebutting the article. David found many of these statements to be factually lacking, but still felt compelled to counter them in tweets of his own. Hours passed. Soon the afternoon was lost, and David was left frustrated by the challenge of making cogent arguments in 140 characters or less (Twitter’s limit).
The solution:David didn’t want to ‘Protect’ his tweets because he believed that the openness and public nature of the service are central to the Twitter concept. David should have considered that this openness means people he knows nothing about can see his tweets and the things he links to.
Second, when it became clear that David had become involved in a protracted debate with another Twitter user who wasn’t making much sense, he should have blocked that user by going to the person’s profile and clicking Block next to the person’s user name. Problem solved. Afternoon saved.
The Story of ‘Cisco Fatty’
The disaster: Unlike the hypothetical examples in this story, this one is true (see ciscofatty.com). Connor was offered a job at Cisco, the big networking company. While weighing her options, she idly tweeted to her followers that she now had to decide whether the “fatty paycheck” she’d draw from Cisco would justify her “hating the work.” Problem is, a Cisco employee saw the tweet and called her out on it, prompting an outpouring of scorn from the Twitter community, as well as a lot of embarrassment for poor Connor.
The solution: Connor obviously should have protected her Twitter account via the ‘Protect my updates’ check box, as described in “Twitter Never Forgets,” above.
But here’s the larger lesson: Many people keep tabs on Twitter using filtered keywords, especially company names–and the use of the term “Cisco” in her tweet was what killed Connor’s job prospects. A better approach would have been to leave the company anonymous, or–better yet–not to tweet about her job offer at all.
Twitter Commands Reference Guide
Here’s a guide on how to use and understand Twitter’s special commands.
• @username The basic building block of conversations, for public replies to a tweet by the user noted after the @ sign.
• D username For a “Direct message” to only the user in question. “DM” also works.
• RT @username For “Re-Tweet,” or a tweet you want to rebroadcast. Prefaced with the original twitterer’s user name.
The following commands ask Twitter for information or tell it how to behave:
• ON username or OFF usernameTurns mobile phone notifications on or off for a single user. STOP and QUIT will cut off all Twitter SMS messages for all users. Only cell phone notifications are affected.
• FOLLOW username and LEAVE usernameTo see-or stop seeing-the tweets of a user. Twitter displays a drop-down message saying it has carried out your command. However, to truly take them off your list, go to their Twitter profile and click Remove next to ‘You follow username’.
• WHOIS username Pops up a brief amount of information about the user.
• GET username Retrieves a particular user’s most recent tweet.
• STATS Tells you how many followers you have and how many are following you.
Google Adds Site-Filtering Feature to Search Google Search: Block Sites

Ever wish you could keep certain sites from showing up in your Google search results? Thanks to a new feature being rolled out right now, you can. Google announced the debut of a site-blocking search tool via its official company blog on Thursday. The tool is simple to use: When you click on a site in a Google search and then go back to Google — presumably because you weren’t satisfied with what you found — you’ll see a new option on the results page to block the site from future searches. All you have to do is click it, and the site will never show up for you again.
Your search site-blocking preferences are saved in your Google account, so you’ll have to be logged in for the feature to work.

And don’t worry: Your search-blocking changes aren’t set in stone. Anytime a site is omitted from a search because of your blocking, Google will display a small message letting you know something’s been removed. You’ll have an option to unmask the hidden results, if you’re so inclined. You can also manage your virtual blacklist via your Google search settings.
The Google search-blocking feature will become available to everyone over the next few days. As of now, it’ll function only in English and only for users on Chrome 9 or higher, Internet Explorer 8 or higher, and Firefox 3.5 or higher.
Google Search Filtering: The Bigger Picture
If this whole thing has you feeling a sense of déjà vu, don’t worry: You aren’t losing your mind. Google announced a similar search-filtering feature about a month ago in the form of an extension for the Chrome browser. The extension did almost the same exact thing as this new feature, except for the fact that it worked on the browser-level instead of on Google’s own servers.
It’s all part of Google’s steady efforts to combat the presence of search spam — a fancy term for low-quality entries that show up in search results. Google has increasingly come under fire for search spam in recent weeks, with some bloggers and pundits saying the company’s level of search-result junk is spiraling out of control. The concerns revolve largely around so-called “content farms,” or sites that generate lots of pages with little real value. Many of these sites monitor popular search queries and create pages for the sole purpose of attracting traffic, even though they have no original or relevant content to offer.
Google also recently adjusted its search algorithm to try to keep those sites from cluttering up results. The change, announced in late February, is designed to reduce rankings for low-quality sites and give higher rankings to sites with more original and in-depth material.
Hands on with Google Handwrite, Google’s new search feature
Newton fans, rejoice: If you like writing your queries on a screen rather than typing them on a virtual keyboard, Google’s new project, Handwrite, should awe and delight.
Announced on Google’s blog Thursday morning, the company’s new beta project aims to make it easier to search, no matter where you are or what you’re doing. Handwrite allows you to block print or handwrite letters, words, and punctuation on the screen, where it will be instantly analyzed and converted into a search term.
The feature is pretty simple to turn on: On an iPhone, scroll down to the Settings link on Google.com (on an iPad, click Search Settings from the Gear icon), enable Handwrite mode, then return to Google.com. Tap the new button in the lower right corner—it resembles a cursive lower-case g—to turn Handwrite on, and just start scribbling.
On an iPhone or iPod touch, I found Handwrite a little finicky due to the small screen. (See my hands-on video, below.) The service will intelligently try to guess at your letters and words, though, so if you only write “dowag” before you run out of room, you can continue with “er” and it will put the letters together to make “dowager”—and suggest you might be looking for the Dowager Countess from Downton Abbey, at that.http://www.youtube.com/embed/iwZOhhul0YU?feature=player_embedded
On an iPad, using Handwrite is a dream, especially if you use a stylus. There’s no worry of real estate crunch, and you have much more freedom in forming your letters.
Unfortunately, I found that Google’s recognition engine was much poorer at analyzing cursive lettering than it was at block printing. I’m not sure whether that has to do with my own messy style of cursive or the engine itself, but I often found it dropping letters (it didn’t know what to do with a lower-case s or r) or misunderstanding words entirely. Luckily, Google’s search engine is good enough to more or less pick up the slack (turning “teasures” to “treasures,” for example), but it’s still a little annoying.
For a beta feature, though, Handwrite is great fun, and something I could actually see myself using pretty often. My handwriting’s slow—but not as slow as my virtual keyboard touch-typing.
Post Credit:
For more Macintosh computing news, visit Macworld. Story copyright © 2011 Mac Publishing LLC. All rights reserved.
Funny Gallery Gif Images For Your Blog
Copy the code of any of your favorite image below and paste it where your want it to display.
Note: Use the Javascript/Html widget to add this images on your Blogger sidebars and various widget section.

Name: Lady Coffee
File type: Gif Image
Size: 77.08 KB (78,926 bytes)
Dimension: 320px × 150px
Image Code:
<img src=”https://ewtnet.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/KJYss1.gif” title=”Lady Coffee” alt=”Elites World Of Technology Images” /><br /><a href=”https://ewtnet.com/2012/07/funny-gallery-gif-images-for-your-blog.html” rel=”dofollow”>Get Image</a>
Name: Roflcon Summit
File type: Gif Image
Size: 669.34 KB (685,409 bytes)
Dimension: 283px × 320px
Image Code:
<img src=”https://ewtnet.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/RINrg.gif” title=”Lady Coffee” alt=”Elites World Of Technology Images” /><br /><a href=”https://ewtnet.com/2012/07/funny-gallery-gif-images-for-your-blog.html” rel=”dofollow”>Get Image</a>

Name: Shake It Off
File type: Gif Image
Size: 792.02 KB (811,027 bytes)
Dimension: 427px × 240px
Image Code:
<img src=”https://ewtnet.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/dLx5t.gif” title=”Lady Coffee” alt=”Elites World Of Technology Images” /><br /><a href=”https://ewtnet.com/2012/07/funny-gallery-gif-images-for-your-blog.html” rel=”dofollow”>Get Image</a>

Name: Keyboad Wars
File type: Gif Image
Size: 306.06 KB (313,407 bytes)
Dimension: 320px × 192px
Image Code:
<img src=”https://ewtnet.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/tumblr_lpq12sSaAR1qa02x4o4_500.gif” title=”Lady Coffee” alt=”Elites World Of Technology Images” /><br /><a href=”https://ewtnet.com/2012/07/funny-gallery-gif-images-for-your-blog.html” rel=”dofollow”>Get Image</a>

Name: Shake It Off (x)
File type: Gif Image
Size: 301.85 KB (309,090 bytes)
Dimension: 320px × 180px (scaled to 320px × 179px)
Image Code:
<img src=”https://ewtnet.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/uFdbj.gif” title=”Lady Coffee” alt=”Elites World Of Technology Images” /><br /><a href=”https://ewtnet.com/2012/07/funny-gallery-gif-images-for-your-blog.html” rel=”dofollow”>Get Image</a>
 Name: Shoo!File type: Gif ImageSize: 344.04 KB (352,294 bytes)Dimension: 320px × 184px (scaled to 320px × 183px)
Name: Shoo!File type: Gif ImageSize: 344.04 KB (352,294 bytes)Dimension: 320px × 184px (scaled to 320px × 183px)
Image Code:
<img src=”https://ewtnet.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/tumblr_lneonzPELX1qbvaudo1_500.gif” title=”Lady Coffee” alt=”Elites World Of Technology Images” /><br /><a href=”https://ewtnet.com/2012/07/funny-gallery-gif-images-for-your-blog.html” rel=”dofollow”>Get Image</a>
Name: Man In Blues
File type: Gif Image
Size: 474.18 KB (485,559 bytes)
Dimension: 196px × 181px
Image Code:
<img src=”https://ewtnet.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/thats-a-penis.gif” title=”Lady Coffee” alt=”Elites World Of Technology Images” /><br /><a href=”https://ewtnet.com/2012/07/funny-gallery-gif-images-for-your-blog.html” rel=”dofollow”>Get Image</a>
Twitter Back Up After Pre-Olympics Crash
Twitter is up-and running for most users after the micro-blogging site was shut down for more than 90 minutes earlier today.
The Twitter shutdown affected users around the world.

Apica, a web performance monitoring company, said twitter crashed at approximately 11:23 a.m. EDT, returned momentarily around 12:04 p.m, and then crashed again at about 12:15 p.m.
The site was back online for most users around 1:30 p.m., though Apica noted that some “users along both coasts continue to experience problems connecting.”
As of 2:45 p.m.. Twitter had not disclosed the cause of the outage on its Status Page.
The company, though, did acknowledge that some users are still affected by the outage. “Our engineers are currently working to resolve the issue,” it said.
Twitter did not respond to a request for comment ont he outage.
Once the site was back online, twitter users were quick to express their frustration with the outage.
“Twitter, do not crash again, please,” wrote @missbanshee. @OwenJones84 tweeted: “Where were you in the Great Twitter Crash of 2012.”
And @john_mcguirk joked: “Twitter could have warned me about this outage before I made that sandwich I was so looking forward to tweeting about.”
The crash came a day before the opening ceremonies at the Summer Olympics in London, which is expected to be a prime subject on social networks in the coming days.
In fact, twitter has created a special page to aggregate tweets from Olympic athletes, coaches and their families, along with sports reporters and announcers.
The Twitter.com/#Olympics page went live today.
For more enterprise computing news, visit Computerworld. Story copyright © 2011 Computerworld Inc. All rights reserved.
Organs on a Chip: Harvard Plans to Recreate the Human Body on Silicon
One day, pharmaceutical companies might not have to test new drugs on animals or even humans. Instead, drugs could be tested with organ-on-a-chip technologies. These are not silicon chips that simulate organs or organisms, mind you; they contain real living, human tissue.
The Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University is going even further with its organ-on-a-chip research by linking up 10 of these individual chips to simulate the entire human body.
Wyss Institute’s Human Lung-on-a-Chip (top) and Human Gut-on-a-Chip (bottom). [Credit: Wyss Institute]
These organ chips are made with a silicon polymer with microfluidic channels carved into them. The channels are filled with human cells, as well as pumps and other mechanical elements that move the cells to replicate the movement of the actual organs.
The lung-on-a-chip, for instance, contains an air sac, a layer of lung cells, a separating membrane, and a blood channel that contains red blood cells. The chip can be connected to a vacuum pump that expands and contracts the organ like the real thing.
The Wyss scientists also produced a gut-on-a-chip that contains intestinal cells that writhe like a human gut going through the motions of peristalsis (pushing food though).
The idea is to replicate the function and composition of an organ on a chip that can be easily tested in order to study effects of diseases, toxins, and pharmaceuticals. The system could provide faster and more accurate human drug testing results than the slower, inaccurate process provided by animal testing.
http://player.vimeo.com/video/29463381?title=0&byline=0&portrait=0
The Wyss Institute recently announced it has entered into a $37-million cooperative agreement with DARPA to create a system that integrates 10 organ-chips to create a complete human-on-a-chip system. The researchers are already well onto their way in develop a chip that mimics the heart, bone marrow, and the human kidneys. With a complete human imitating system, scientists could see the biochemical effects of drugs across the entire human body.
Facebook’s Recommendations Bar: A Privacy Concern?
 Facebook has rolled out a new feature called the Recommendations Bar for website owners. The Recommendations Bar allows website owners to tap into the social network’s database of what you and your friends read, share, and like.
Facebook has rolled out a new feature called the Recommendations Bar for website owners. The Recommendations Bar allows website owners to tap into the social network’s database of what you and your friends read, share, and like.
Here’s how it works: as you read a story on a website that has the Recommendations Bar feature activated, you’ll see pop-up windows in the bottom right corner of the page. The pop-up window will contain stories from the website that your Facebook friends have shared or liked. The window also contains a Like button, allowing you to like the story without ever leaving the website.
Also Read: How to install Facebook Recommendation Bar In Your Blog
Several sites already use this feature, including the tech blog Mashable, entertainment site Wetpaint, and U.K.-based tabloid The Mirror. Recommendations are limited to articles on the website that were shared by Facebook users. Websites using the new feature reportedly see as much as three times as many clicks on stories that are recommended in the pop-up boxes.
This feature obviously benefits the website owner, but what’s the benefit to you? There isn’t really one–it’s just another reason to be worried about your privacy on the social networking site.
Don’t get me wrong–relevant recommendations from friends might be helpful. There’s a good chance that the recommended content will be something that we’ll be interested in reading, since we often pick our friends based on shared interests.
But there’s another side to this issue, and that’s the potential privacy concern. When Facebook debuts services that share, without your explicit permission, what you’re doing online…well, it always seems to go south.
In May, my colleague Sarah Jacobsson Purewal noted this issue regarding Facebook’s social reader apps. She said these types of features create a “giant circle of awkward oversharing that people have little control over.” Who knows–what you’re reading might reveal things about yourself that you’re not necessarily willing to share with the world.
Since there’s no way to control what type of content is shared, except to not share or like it altogether, your personal reading habits will be on display for all your friends. The only positive here is hat, unlike Social Reader, you physically need to take action on Facebook–whether you share or like the story–for it to show up in the Recommendations Bar.
How To Add Facebook Recommendations Bar To Blogger
Finally, Bloggers can keep readers to their site by using this fantastic recommendation bar.
It’s designed to display additional recommended articles right after readers have finished reading an article or spent some time on your blog. It will collapse on page load and expand once a reader has reached a specific location on your blog or finished reading the post.
Only those articles are displayed that are previously liked or shared on Facebook. The number of likes are displayed under each article along with page title and a thumbnail. It also contains a like button and previously contained an Add to Timeline button that has been removed now.
Unlike Facebook Recommendations box which offered related stories but with lack of user friendly interface and engagement, Facebook bar will force readers to stay longer on your site leading to increased pageviews, page impressions and thus traffic.
HOW TO INSTALL ON BLOGGER
This widget works on both blogger blogs and wordpress blogs. Now i’m going to take you true on how to add it on your blogger blog, the amounts of comment i get will determine if i’m going to show the wordpress tutorial. follow this simple steps to add on blogger:
Step1: Create a Facebook Application
For this plugin to work you will need to create a Facebook App in seconds. The below method is the standard and correct method for creating any FB App you like.
- Log into Facebook Apps
- Click on Create New App button towards Top-right
- In the box that pops up, type “My Recommendation Bar” inside the App name field and leave other options as default. Click continue.

4. Enter the captcha security code. Click Submit
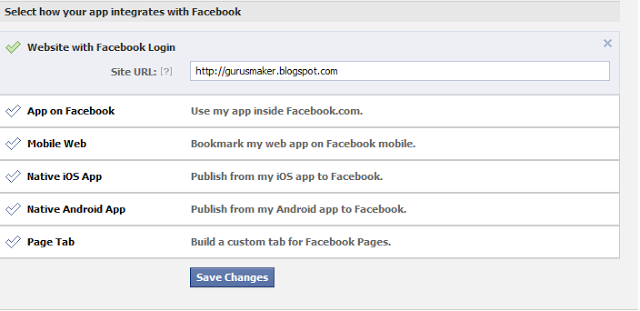
5. You are app is almost complete. Just click Website with Facebook Login tab and inside the box input your blog URL. See the screenshot below. Do not touch remaining options and click Save Changes.
6. You will see two strings of alpha-numerical characters. One is App ID and the other is App secret. Just copy the App ID code and keep it save in a notepad. We will need it later.
Congrats App finally created! Lets proceed to step2.
Step2: Add “Recommendations Bar” To Your Blog
Follow these steps to add the bar to Blogger:
- Go to Blogger > Template
- Backup your template
- Click Edit HTML > Proceed
- Search For this : <html
Replace it with this code:
xmlns:fb=’http://ogp.me/ns/fb#’
This will make the plugin compatible in older versions of internet explorer also. Since blogger templates are coded in XML therefore inserting this XML namespace will enhance the plugin performance and compatibility.
5. Next search for <body> and just below this tag paste the following code:
Note: If you are using the new blogger templates like Simple, Awesome Inc., Travel, Watermark or Picture window then please search <body for instead. Make sure to paste the code below the entire body tag.
</p> <div id=’fb-root’></div> <p> <b:if cond=’data:blog.pageType == “item”‘></b:if><b:if cond=’data:blog.pageType != “static_page”‘></p> <div style=’z-index:999999; position:absolute;’> <fb:recommendations -bar action=’like’ max_age=’0′ num_recommendations=’3′ read_time=’10’ side=’right’ site=’https://ewtnet.com’ trigger=’40%’></fb:recommendations></div> <p></b:if>
You are almost done. Make these changes:
- Replace *************** with your 15 digit App Id that you saved in step1.
- Replace http://www.gurusmaker.blogspot.com with your blog link
6. Save your template and you are all done!
Visit your blog and scroll down about 50% of your page and wait for 10 seconds for the plugin to expand. Enjoy the new way of free pageviews juice! 🙂
Optional Steps
Below are optional customization and control options. You can skip them if you want max_age: will decide the age limit of articles. Sometimes you don’t want to display too old articles so you can set it to display up to 1-180 days old posts. But if you don’t want to take age into account then let it be 0 as default. num_recommendations: You can set how many articles to display. By increasing or decreasing the value 3
read_time: As soon as the user reaches a specified location, the plugin would expand and before expanding it will take some time. I have kept it equal to 10 seconds, you can increase it to 30 or more as you wish. side: You can decide the location of plugin. By default it shows up towards the bottom right corner of your page. You set it to float to left trigger: On page load the plugin collapses and as soon as it reaches a specified location it expands. You can choose that location in three ways i.e. onvisible, X% or manual. I prefer locating the trigger point by percentage for better pageviews. The widget will expand as soon as the user scroll downs 40% of your page. You can increase or decrease this value. If you wish that the plugin must expand as soon as the reader reaches the end of your article then instead of pasting the code between the purple lines paste it just below data:post.body tag and use the value onvisible instead of 40%. The widget will display only on post pages and not on homepage or static pages. To display it on all pages, then simply delete the purple bolded lines
Researchers Develop Solar Panels That Still Let the Sunlight Through
In the last year, we’ve seen scientist try to put photovoltaic materials everywhere–the paint on your walls, in space, and even your coffee table. Now, a team of researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and the University of California, Santa Barbra (UCSB) has developedtransparent solar panels that could be used as power-generating windows for your house. The new transparent solar panels are a flexible, plastic cell that pulls energy exclusively from the infrared spectrum of the sun’s rays. At the same time, the panels allow the visible light to pass though pane that’s nearly 70 percent transparent. Previous attempts at developing transparent solar panels have always resulted in a poor balance between efficient energy production and transparency. These researchers, however, developed a special recipe that’s achieved a 4 percent power-conversion efficiency rate while being the most transparent solar panel ever created. 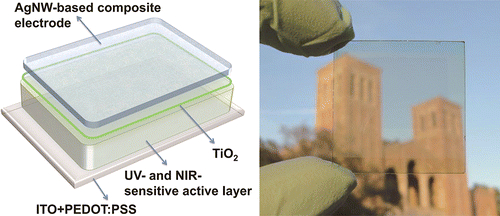 [Credit: ACS Nano]The researchers created the clear solar panel by using a polymer that’s sensitive to near-infrared light overlaid with a silver nanowire composite as a transparent electrode. The biggest breakthrough of the research was the creation of a transparent electrode, produced by mixing silver nanowires with titanium dioxide nanoparticles, to replace the opaque metal electrode that was used in the past. Polymer solar cells are a particular item of great interest because they are lighter, more flexible and potentially cheaper to produce at high volume than traditional solar panels. If the scientists work out a way to mass-produce their clear solar cells, the cells could be integrated into every home, skyscraper, car, and mobile device. [UCLA and ACS Nano via Extreme Tech]
[Credit: ACS Nano]The researchers created the clear solar panel by using a polymer that’s sensitive to near-infrared light overlaid with a silver nanowire composite as a transparent electrode. The biggest breakthrough of the research was the creation of a transparent electrode, produced by mixing silver nanowires with titanium dioxide nanoparticles, to replace the opaque metal electrode that was used in the past. Polymer solar cells are a particular item of great interest because they are lighter, more flexible and potentially cheaper to produce at high volume than traditional solar panels. If the scientists work out a way to mass-produce their clear solar cells, the cells could be integrated into every home, skyscraper, car, and mobile device. [UCLA and ACS Nano via Extreme Tech]
Tablets, According to Staples
 Amazon Readying Mulitple New Kindle
Amazon Readying Mulitple New Kindle
Amazon has big plans for its coming onslaught of tablets to compete with Apple’s iPad and Google’s Nexus 7. Reuters reports Staples US Retail president, Demos Parneros as saying there are five or six upcoming tablets, among them a a 10-inch model. That 10-inch model would clearly be positioned against iPad, as well as a plethora of Android tablets. Rumors about a bigger Kindle Firehave been circulating for some time, but since Staples sells the Kindle Fire, this 10-inch model is a bit more believable now.
Amazon’s first-generation Kindle Fire.According to previous reports from BGR, the 10-inch Kindle Fire will be feature-packed with a quad-core processor, front-facing camera, microUSB port, and possibly an HDMI-out port. The new tablet will apparently be a major step up from the current Kindle Fire in terms of appearance and design.
Other Upcoming Kindle Fires
The original Kindle Fire tablet which Amazon debuted in September last year is due for a refresh any day now (rumors point to the end of July), so we could count the 7-inch Kindle Fire 2 as one of those other many tablets Amazon has planned. It’s not clear if the five to six tablets Pareneros mentioned are actually really two tablet models (a 7-inch and a 10-inch) with different storage options or even display resolutions—or if another Kindle Fire size is coming too. The Kindle Fire has a 1024 by 600 pixel resolution, but NPD DisplaySearch recently told CNet about an additional 7-inch model with 1280 by 800 pixels resolution—on par with the flying-off-the-shelvesGoogle Nexus 7. That high-resolution display will help make the Kindle better suited for reading. NPD DisplaySearch analyst Richard Shim also noted he expects an 8.9-inch Kindle Fire 2 with a 1920 by 1200 pixels full-HD display. It might not be the iPad’s (2048 by 1536 pixels) retina display, but the bump in pixels would certainly make the Kindle Fire more competitive. Digitimes alsoreported an 8.9-inch Kindle Fire is coming. Whatever this bunch of Kindle Fire tablets turn out to be, tablet wars will be in full swing before the holidays.
Streaming Services Increase Pressure on TV
More choices in original programming are surfacing on Hulu and PlayStation 3. Who needs TV? The assault on traditional TV continues. While things over in the Netflix camp have been relatively quiet (their last big news was that Breaking Bad Season 4is now available for streaming) Hulu has continued to announce new shows.

For instance, last week Larry King returned to the small screen with the launch of Larry King Now on Hulu. King says (on Hulu’s blog) that it was the capturing of Osama Bin Laden that convinced him to come out of retirement. When coverage was all over the airwaves and King wasn’t part of it, he missed the rush and knew he had to get back in the business.
Dramatic story, but I’m not sure how it fits in with his first guest being Family Guy’s Seth MacFarlane. We’ll see what kinds of guests King on Hulu can draw.

Hulu has also announced its first international co-production. It is partnering with the BBC to produce a fourth season of satirical comedy show The Thick Of It. If, like me, you’re unfamiliar with the series you’ll be happy to learn that Hulu will start running the first 3 seasons on July 29.PaidContent has more info. Stepping away from Hulu, Sony has announced another streaming app coming to the Playstation 3. This time it’s The Laugh Factory. This app will offer stand-up routines from the Hollywood-based comedy club of the same name. It goes live on September 1 and will be free for all PS3 owners until December. After that it’ll cost $3/month.

Some PS3 owners seem to be skeptical of that monthly fee. I’m not much of a comedy fan (anyone will tell you I have no sense of humor) so it’s hard for me to judge the value. That seems pretty cheap even if a lot of the content can be found for free by searching YouTube or wherever. The convenience of having it all queued up on the PS3 seems like it’d be worth $3 to me, but I guess we’ll see. More info is available on the Playstation Blog. The other day I speculated that perhaps Sony was ramping up their video streaming efforts in response to Microsoft doing the same. Three new channels (NeonAlley, CrunchyRoll, and The Laugh Factory) in three days is a good start.
For more computing news, visit ITworld. Story copyright © 2011 ITworld Inc. All rights reserved.
Firefox 15 Beta Tackles Memory Leaks
Mozilla has released a beta version of the next version of its Firefox browser with better memory management and significant speed improvements.  “Firefox 15 prevents most memory leaks caused by add-ons, including Firebug,” Nicholas Nethercote writes in a Mozilla blog. Firebug is a Firefox add-on for debugging web pages. “For many users with add-ons installed, this will significantly reduce Firefox’s memory consumption, without requiring upgrades to those add-ons,” he adds. “For those users, Firefox 15 is likely to be faster (sometimes drastically so) and less likely to crash, especially if they have multiple add-ons installed and/or keep Firefox running for a long time between restarts.” Nethercote explains that add-on memory leaks are caused by “zombie compartments,” where information from web pages is stored and remains after you close a page or depart from it. Firefox 15 cleans out those compartments, a move that its developers weren’t entirely sure would work. Much criticism has been leveled at Firefox since its inception over its piggish memory practices, but in recent months it has made great strides in its memory management. Last November, for instance, it put SpiderMonkey, the Javascript engine used by the browser, on a diet. And in May, it announced its campaign to plug memory leaks in add-ons.
“Firefox 15 prevents most memory leaks caused by add-ons, including Firebug,” Nicholas Nethercote writes in a Mozilla blog. Firebug is a Firefox add-on for debugging web pages. “For many users with add-ons installed, this will significantly reduce Firefox’s memory consumption, without requiring upgrades to those add-ons,” he adds. “For those users, Firefox 15 is likely to be faster (sometimes drastically so) and less likely to crash, especially if they have multiple add-ons installed and/or keep Firefox running for a long time between restarts.” Nethercote explains that add-on memory leaks are caused by “zombie compartments,” where information from web pages is stored and remains after you close a page or depart from it. Firefox 15 cleans out those compartments, a move that its developers weren’t entirely sure would work. Much criticism has been leveled at Firefox since its inception over its piggish memory practices, but in recent months it has made great strides in its memory management. Last November, for instance, it put SpiderMonkey, the Javascript engine used by the browser, on a diet. And in May, it announced its campaign to plug memory leaks in add-ons.

In addition to better memory management, Firefox 15 also supports theOpus audio format. The format, which can be played directly in Firefox 15, offers better compression formats like MP3, Ogg, or AAC; is good for both music and speech; can dynamically adjust bitrate, audio bandwidth and coding delay; and supports both interactive and prerecorded applications. “We think Opus is an incredible new format for web audio,” Timothy Terriberry writes in a Mozilla blog. “We’re working hard to convince other browsers to adopt it, to break the logjam over a common
format.” The “prime time” version of Firefox 15 is scheduled for avaiability August 28.
Spam Halved With Grum Takedown
An international effort by spam fighters has taken down the infamous Grum botnet, slashing in half the worldwide amount of spam e-mail.  Grum’s last servers were taken offline in Russia last week, effectively killing the botnet that has no fallback mechanism, said Atif Mushtaq, a researcher at FireEye’s security lab, which collaborated with the Russian Computer Security Incident Response Team and the Spamhouse Project in battling Grum. At its height, Grum was the world’s largest spam botnet, since January. Before the takedown, the botnet’s120,000 malware-infected, active computers were spewing 18 billion spam e-mail a day, or roughly a third of the world’s spam, said Trustwave. The impact of Grum’s collapse went beyond the spambot. Stopping Grum caused a slowdown in the world’s largest spam botnet, Lethic, Mushtaq said Thursday. “Due to this [international] community reaction, Lethic has gone underground for awhile.” With Grum down and Lethic quiet, the total amount of the world’s spam has been cut in half, at least temporarily, said Mushtaq. Aside from the numbers, the spam-fighters’ success is expected to have a chilling effect on Russian and Ukrainian spam operations, which can no longer assume the countries offer a safe haven, due to weak laws.
Grum’s last servers were taken offline in Russia last week, effectively killing the botnet that has no fallback mechanism, said Atif Mushtaq, a researcher at FireEye’s security lab, which collaborated with the Russian Computer Security Incident Response Team and the Spamhouse Project in battling Grum. At its height, Grum was the world’s largest spam botnet, since January. Before the takedown, the botnet’s120,000 malware-infected, active computers were spewing 18 billion spam e-mail a day, or roughly a third of the world’s spam, said Trustwave. The impact of Grum’s collapse went beyond the spambot. Stopping Grum caused a slowdown in the world’s largest spam botnet, Lethic, Mushtaq said Thursday. “Due to this [international] community reaction, Lethic has gone underground for awhile.” With Grum down and Lethic quiet, the total amount of the world’s spam has been cut in half, at least temporarily, said Mushtaq. Aside from the numbers, the spam-fighters’ success is expected to have a chilling effect on Russian and Ukrainian spam operations, which can no longer assume the countries offer a safe haven, due to weak laws.
Security Teams Unite to Fight
The Grum operation was done without any involvement by law enforcement, showing that security researchers working together can also be effective in fighting botnets, which besides spam are used in denial of service attacks against websites.

With security researchers globally watching them, cybercriminals now have to deal with far more adversaries than in the past. “That will have a huge impact on the mindset of bot herders, and that may be the reason Lethic is going underground,” Mushtaq said. Bot herder is the name given to people who control hijacked computers, or bots, in an illicit network. Grum’s death leaves tens of thousands of inactive, malware-infected computers. But without the original master computer and the IP addresses of the infected systems, the botnet is unlikely to be resurrected. “There’s no way to hijack this botnet,” Mushtaq said. “[the computers] are lost to us and to bot herders.” The Grum-killing operation started about two weeks ago when authorities in the Netherlands pulled the plug on two servers. This led to other servers in Panama being taken offline early this week. In a cat-and-mouse game with spam fighters, the Grum operators launched more servers in Russia and the Ukraine. A service provider in Russia took the last of those computers off the Internet on Wednesday. How long spam numbers will remain down is unclear. Spammers are sure to start filling the gap at some point. “Major takedowns can have a perceptible impact for weeks, even months, but that doesn’t mean it will be the case here,” David Harley, senior research fellow at ESET, said in an e-mail.